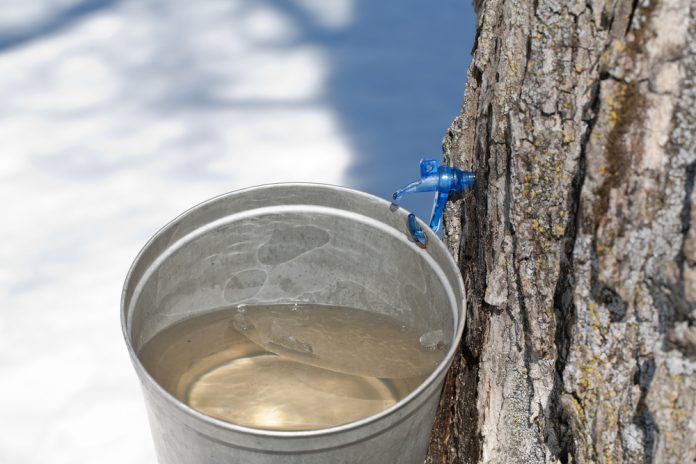
Even though Europeans knew how to tap trees, do you know, it was the American Indian who discovered how to make maple syrup? (Around 1660)
The sap was considered to be a fortifying drink, since birch sap includes fructose, glucose, fruit acids, amino acids, vitamin C, potassium, calcium, phosphorous, magnesium, manganese, zinc, sodium and iron. Both sap substances are digestible by the human body (as opposed to other parts of the tree-containing cellulose: non-digestible).
There are also numerous accounts of the mountain people [Montagnais], who eat the maple’s inner bark to fight hunger during a famine. He describes maple water as honey-like, sweet sugar.
Birch sap is commonly known for its diuretic properties, detoxifier, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, diuretic, cleansing and purifier. Diuresis activation helps eliminate organic waste such as uric acid, and cholesterol. Birch sap is also known to aid in joint and bone health, hair loss, arthritis, kidney stones and weight loss. (Source)
Birch sap is collected only at the break of winter and spring so NOW is the perfect moment to extract the sap (mid-February to mid-April). It is a clear, uncolored liquid when fresh, very similar to water, often slightly sweet with a slightly silky texture. After two to three days, the sap starts fermentation and the taste is more acidic (but naturally fermented birch sap can also be consumed).
The Birch Family


Birch sap hasn’t remained fresh for long. When tapping a tree, be sure to use the sap within a few days for its intended purpose. Do not make the mistake of thinking you can tap now and proceed later-this will affect the Birch sap’s taste and chemical properties. Birch syrup on the other hand has a shelf life of around two years – but it takes about 130–150 gallons sap make to make one gallon syrup.
Related: How to Make Apple Cider Vinegar
The Maple Family


The Walnut Family


‘Black walnut syrup is liquid gold’ says Michael Jaeb, Millersburg owner of Basic Gourmet Syrups, Ohio. He sells $15.75 per 8-oz of the rare syrup. Bottle and it’s never enough.
Black walnut syrup needs a premium price in part because the black walnut trees produce just about one-third of the sap maple trees. The sugar content of the sap is about the same – it takes about 40 gal. of sap to make 1 gal. of syrup. One consideration in making black walnut syrup is that the trees are often highly prized for their lumber value; and tapping could detract from the commercial value of the logs.
The Sycamore Family


Like birch, you can tap on sycamore all year long.
The sycamore and sweet gum tree both belong to the same family and are very common in the South. Sycamores are often confused with Cottonwood trees, looking at the leaves is the way to distinguish them. Sycamores have dot-lobed leaves, while cottonwood has almost heart-shaped leaves that are round. The sweet gums are also easy to recognize. They have a thick coarse bark with leaves which are very similar to the sycamore. They are most easily identified by their nuts or “gumballs”, golf-ball sized balls that are hollow with many holes and little spikes protruding all over the ball.
To protect the tree’s health; do not put taps in any tree smaller than 10 inches in diameter.
Over-tapping damages the trees, undertapping reduces the yield of sap without doing anything positive for the trees. A commercially profitable sugar business should have a woodland of 70-90 taps / acre and 20 + acres. Taking care of the trees — according to the guidelines, clearing competition from the sap trees, pruning dead branches, etc.—is a good practice of management. Aim for 25-30 productive trees per hectare of sugar bush.
People will turn back to the old ways of surviving during a crisis, just like the one you’ve just read. Crisis can last for up to a couple of years, and don’t think it can happen in the US. You are only nine meals away from anarchy if the grocery shelves are empty.